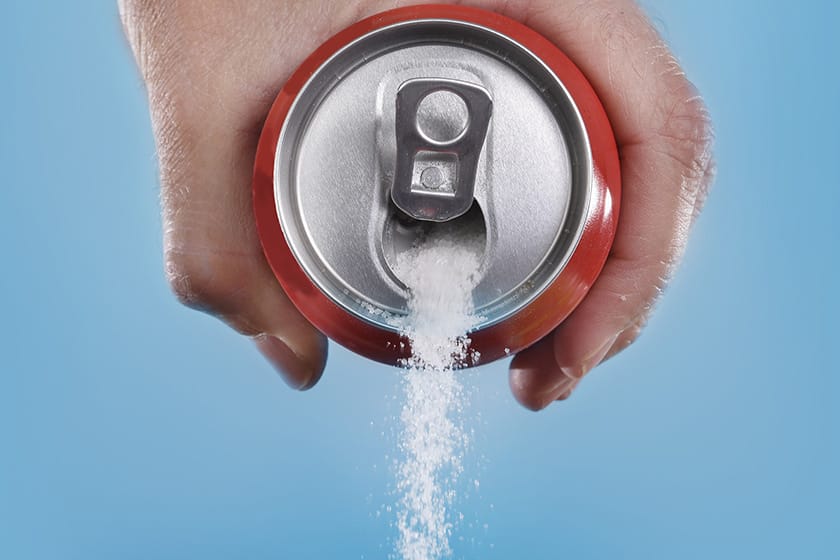
Sugar-sweetened drinks raise the risk of cardiovascular concerns, despite physical exercise
In the ever-evolving field of nutrition science, a compelling piece of research recently featured in the Current Developments in Nutrition journal meticulously combed through 20 clinical trials to decode the cardiovascular implications tied to our drink choices[1]. The drinks under the microscope included a broad spectrum from the morning ritual of tea and coffee, the mid-day boost from fruit juices and energy drinks, to the evening unwind with alcohol, and the ubiquitous presence of sugar-sweetened...